Design and Planning Key Points of Food Microbiology Detection Laboratory - Nanjing Expansion Technology
Release time:
2025-07-01 14:49
In food microbiology testing, laboratory design and planning are the foundation for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of test results and the safety of laboratory personnel. Nanjing Expansion Technology With years of experience in laboratory construction and relevant standards and specifications, we will analyze the key design points of food microbiology testing laboratories for you.

Laboratory Zoning and Functional Setting
According to the provisions of CNAS-CL09:2013 "Application Instructions for the Accreditation Criteria for Testing and Calibration Laboratories in the Field of Microbiology Testing" in "5.3 Facilities and Environmental Conditions", the construction of food microbiology testing laboratories must meet the needs of testing work, with obtaining reliable test results as the core, while also meeting the corresponding biosafety level requirements. Based on this, the main functional zones of the laboratory are as follows:
- Preparation Room :Responsible for weighing, preparing, and storing culture media. Balance rooms and water preparation rooms can be incorporated into this area. According to the actual functions and area size, the preparation room can be further reasonably divided to improve operational efficiency.
- High-Temperature Room :Used for moist heat sterilization of culture media, dry heat sterilization of glassware, etc. This area should remain independent and preferably equipped with exhaust facilities to ensure the safety of the experimental environment.
- Clean Room :This is a key area for sample testing, where all sample pretreatment is performed. Its environmental control directly affects the accuracy of sample testing and requires strict control of indicators such as cleanliness.
- Incubation Room :Specifically used for placing incubators to meet the needs of food microbiology testing for various incubation temperatures. It is recommended to also place the water bath required for incubation here. It is particularly important to note that mold cultivation should be separated from bacterial cultivation, and institutions engaged in health food registration testing should set up a special mold laboratory.
- Pollutant Treatment Area :Harmless treatment of processed samples, intermediate cultures, and various wastes contacted during the identification of suspected bacteria to prevent pollution spread.
- Washing Room :Washing, drying, and storing harmlessly treated glassware to ensure the cleanliness of experimental glassware.

In addition to the above main functional areas, the laboratory also needs to be equipped with a reagent and consumable storage warehouse for storing glassware, protective equipment, reagents, consumables, and culture media with a large turnover; a sample storage area for placing tested and untested samples; and space for intermediate cultures and standard strains.
Laboratory Floor Plan Design
A reasonable floor plan can improve laboratory efficiency, reduce management difficulty, and reduce initial investment costs. Conversely, unreasonable layouts will affect the effective use area and bring many inconveniences to experimental work.
The laboratory layout design should strictly follow the "unidirectional flow" principle to reduce and avoid potential pollution and biological hazards. The food microbiology testing laboratory should be designed as an independent area, planned according to the distribution of various functional areas and the unidirectional flow principle, combined with the actual site conditions.
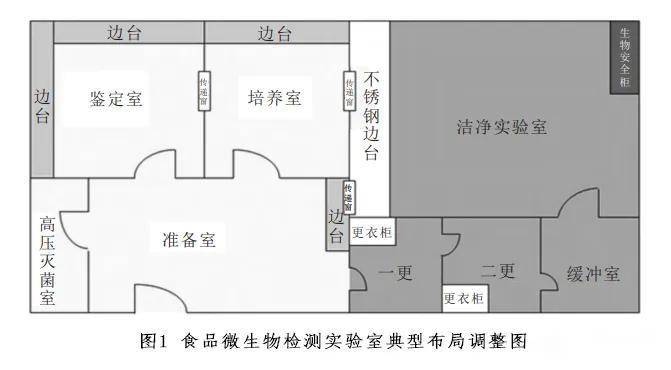
In a typical layout, the preparation room can be placed in the middle, making it adjacent to the clean room, culture room, identification room, and high-pressure sterilization room to ensure a convenient and smooth workflow. Samples need to first enter the clean room, then enter the incubation room, identification room, and finally waste disposal, in order to meet the "unidirectional flow" principle.
In addition, the office area or rest area for testing personnel should be separated from the experimental area, but should not be too far away to facilitate work. Various institutions can reasonably add sample storage rooms, mold laboratories, standard strain storage areas, and warehouses and other auxiliary facilities according to the size of the site.
Key Areas and Precautions
-
Key Area - Clean Room
Sample testing needs to be carried out in a clean area, and both clean benches and clean rooms can meet the requirements. However, clean benches have limited space and are suitable for situations with small sample volumes and simple operations. In actual testing, considering work efficiency, the clean room is a key place for pretreatment of microbiological testing, which can effectively prevent secondary contamination of samples. -
Precautions
- Cleanliness Requirements :Although China currently does not have design specifications for food microbiology clean rooms and there are no clear requirements for cleanliness, generally speaking, a Class 10000 clean room can meet the needs of food microbiology testing. According to GB 50073 "Clean Room Design Specifications", two control particle sizes can be selected for the cleanliness level. For biosafety laboratories, 0.5μm and 5μm should be selected as the control particle sizes. Although the secondary biosafety laboratory does not have requirements for cleanliness, in order to protect the experimental environment and extend the service life of the biosafety cabinet, it is recommended to use mechanical ventilation, install a filter device, and maintain a negative pressure of no less than -5Pa. At the same time, qualified institutions should be regularly arranged to test various technical parameters of the clean room, with the longest testing interval being 12 months, while airborne bacteria and settled bacteria testing is generally 6 months.
- Disinfection and Sterilization System :When building a laboratory, in addition to considering the corrosion resistance of decorative materials and the problem of bacterial growth in temperature and humidity control systems, daily disinfection and sterilization must also be considered. Common sterilization methods for clean rooms include ultraviolet lamp sterilization and gas sterilization. Ultraviolet lamp sterilization is surface sterilization and does not work on the inside and shaded surfaces. Ultraviolet light with a wavelength of 253.7nm has the best sterilization effect, and the ultraviolet lamp illuminance needs to be checked regularly, and the lamp switch should be installed outside the door. If the entire clean room needs to be thoroughly sterilized, gas fumigation methods such as ozone fumigation and peracetic acid fumigation can be used, but effective ventilation is required before personnel enter.
- Selection of Design and Construction Units :The design and construction units should be carefully selected, and the project supervision and acceptance work should be taken seriously to ensure the quality of laboratory construction.
The reasonable layout of the food microbiology testing laboratory and the effective control of the clean room environment are the foundation and guarantee of microbiological testing work. In addition, food microbiology testing, from sampling, sample pretreatment, cultivation, to transfer and identification, is a long and continuous process, which requires laboratory personnel to strictly follow the operating procedures of each link to ensure the objectivity and authenticity of the test results.
Nanjing Expansion Technology focuses on laboratory design and planning, with rich industry experience and numerous industry cases. If you need professional laboratory design and planning services, please feel free to call or contact online customer service.
Related News



